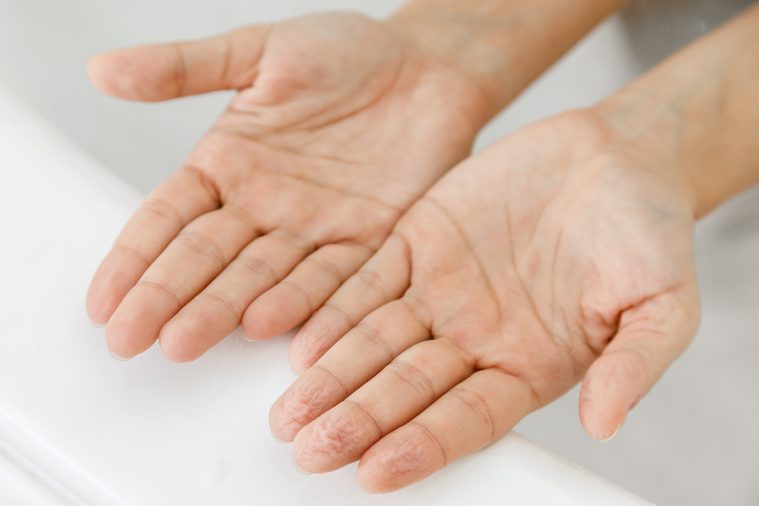
Your fingers wrinkle in the water
Blood vessel constriction is to blame for making your fingers and toes look like prunes after you step out of the shower. As water starts to seep in your skin, the upper layers of the skin swell up. This water permeation causes the nerves in your skin to fire off electrical charges and chemicals, which make the blood vessels constrict. A negative pressure from your narrowed blood vessels pulls down the upper layers of your skin to create the wrinkles you see on your fingertips and toes. “Evolutionary experts are finding evidence that it may have actually helped humans to grip objects better when in water,” says Amy Rantala, MD, family medicine physician at Mayo Clinic Health System in Eau Claire, Wisconsin. “People who have nerve damage to their fingers or toes will often not have this same wrinkling of fingers.” Here are more bizarre bodily functions you just can’t control and the explanations behind them.

Your body jerks right before you fall asleep
An estimated 70 percent of people experience hypnic jerks on a regular basis, that feeling you get when your body suddenly jerks right before you fall into a deep sleep. Research hasn’t been able to pinpoint the exact reason behind the strange phenomenon, but there are a few theories circulating. One of them is that your muscle tone starts to shift as your breathing and heart rate start to slow down along with a body temperature decline, which causes these twitches during the transition. It could also be that the brain sends a signal to your muscles to tense up because it misinterprets the relaxation of your muscles as a sign that you’re falling. Check out these strange body features you never knew existed on humans.

You hear blood pumping in your ears
If you lie down or sit quietly, you may sometimes hear a pulse in one or both of your ears. “We often think of tinnitus as ringing in the ears,” says Dr. Rantala. “But this is a variation where the person feels and hears the pulse in their ears called pulsatile tinnitus.” The sound is typically caused by a turbulent flow in the blood vessels in the neck and head. Pulsatile tinnitus is usually not a cause for concern unless it occurs frequently, which could be a sign of high blood pressure, a blockage in the ear canal, or artery problems near the ear.
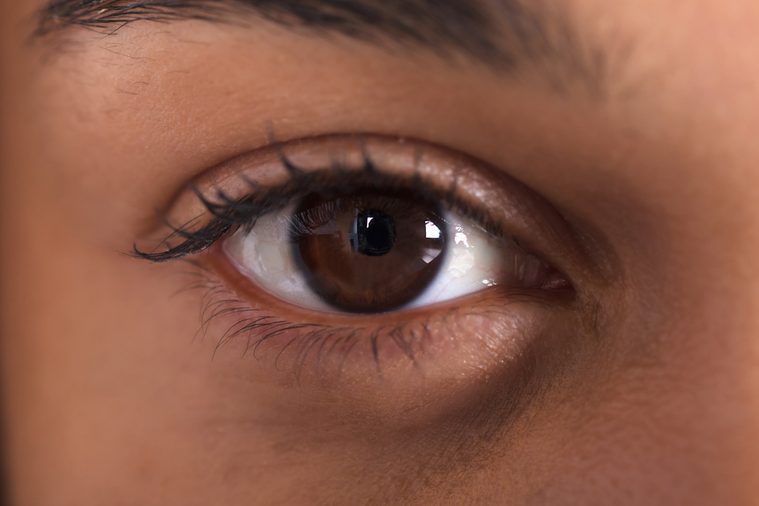
Your eyelid randomly starts to twitch
A twitchy eyelid, known as blepharospasm, often happens randomly and can last anywhere from minutes to days. Most are usually harmless and don’t affect your vision. “We don’t know why this happens exactly but fatigue, caffeine, and stress are common culprits,” says Dr. Rantala. “I often recommend trying to stretch the muscle that is twitching.” This condition will typically go away on its own but if it lasts for more than a couple days, seek a physician immediately. Here are some weird body part names they never taught you in healthy class.
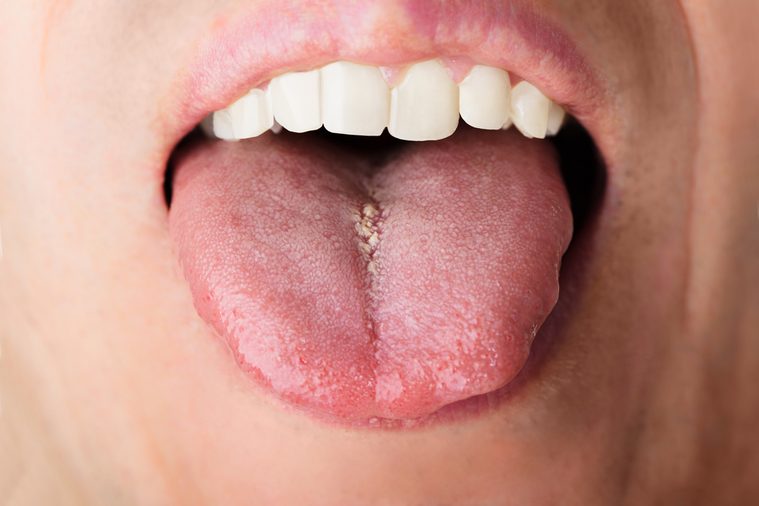
You taste metallic saliva right before you vomit
The copper-like taste you get right before you throw up is your body’s response to the stomach acids that are about to enter your mouth. “That’s water brash,” John F. Kuemmerle, MD, professor in the division of gastroenterology, hepatology, and nutrition at the Virginia Commonwealth University School of Medicine, told Slate. “When things are getting ready to come back up into the esophagus, there is a reflex that causes you to salivate heavily.” Your body produces basic saliva to neutralize the acidity of the vomit. If this metallic saliva happens on a consistent basis, you could suffer from silent reflux, a condition where the stomach’s acidic contents come up into the esophagus.
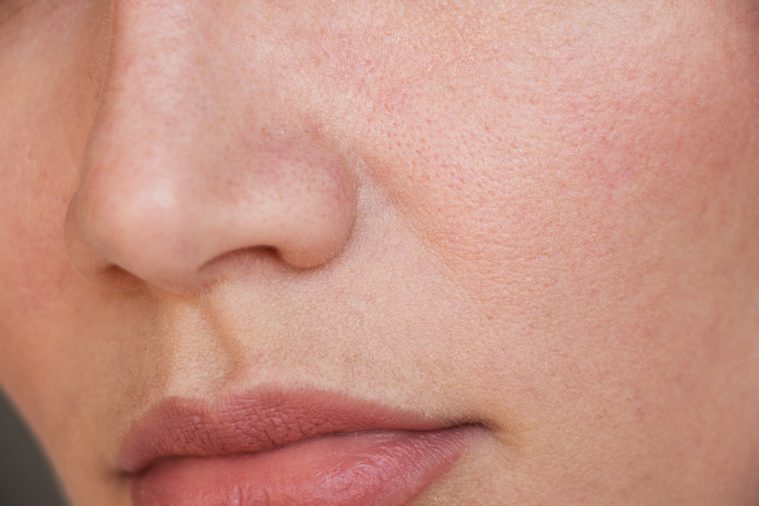
Your nose burns when water goes up it
Cold freshwater is your nose’s worst enemy because the inside of your nose is a salty environment. “The cells in our body have a salinity content,” Stacey Gray, MD, director of the Sinus Center at Massachusetts Eye and Ear told Stat News. “Freshwater doesn’t have any salt in it so it’s very shocking to the inside of our nose when water goes inside.” The nerve endings that line the inside of your nose feel a burning sensation as the nose’s mucous rids itself of the freshwater invasion to restore its natural, salty environment.
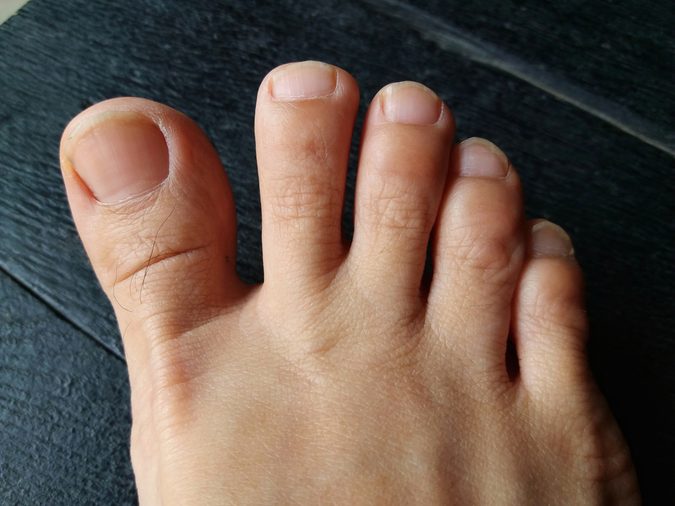
Your nail falls off after a serious injury
If you stub your toe or jam your finger bad enough you could develop a subungual hematoma, which is when blood starts to collect under your injured nail to create a black or purple look underneath. If blood continues to build up under the nail, it may separate the nail from the nail bed and result in it falling off. A large accumulation of fungus or skin cells from the autoimmune condition psoriasis could also cause your nail to fall off. Check out these other signs of disease your feet can reveal.
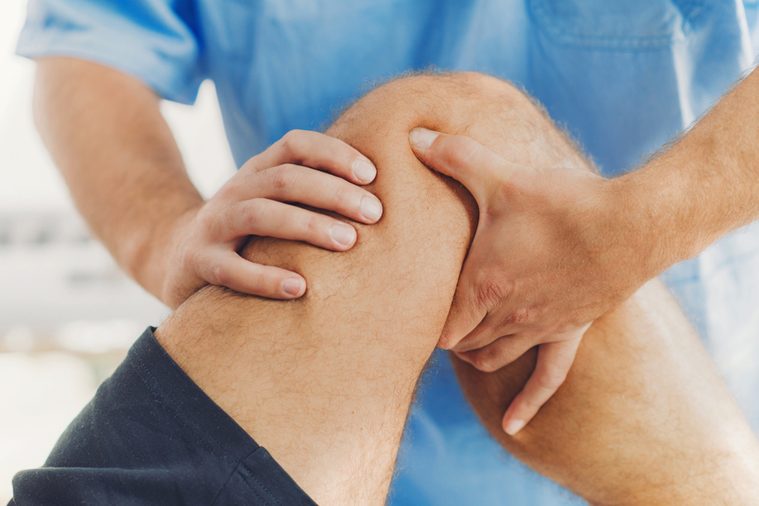
Your knees crack after sitting for a long period of time
It’s normal to hear your joints crack and snap. In fact, the cracks you hear are nothing more than gas being released in between the spaces in your joints. The noises shouldn’t alarm you unless the cracking is accompanied by pain or swelling. Other things like muscles or tendons rubbing against your bone during a workout or cartilage wearing away from age may also make your joints creaky. “We say motion is lotion – the more you move, the more your body lubricates itself,” Kim L. Stearns, MD, an orthopedic surgeon at Lutheran Hospital in Ohio told the Cleveland Clinic. “When you’ve been sitting or lying around, fluid in the joints doesn’t move. The more active you are, the more your joints lubricate themselves.” Make sure you know what to do when your body makes these 10 weird noises.

You hiccup after eating too quickly
Nothing is worse than getting a bad case of the hiccups during a quiet meeting at work. Hiccups are typically short bursts of breathing in that may occur when the diaphragm, a sheet of muscle above the stomach, is irritated. Your diaphragm contracts every time you breathe in. When you eat too fast, your stomach swells up and causes these diaphragm contractions. Thus, a serious case of the hiccups ensues. Learn these quick cures for hiccups to get fast relief.

You get brain freeze from ice cream
No, your brain doesn’t actually freeze! When you consume ice cream too quickly, you’re rapidly changing your throat temperature from warm to cold. The throat is where the two arteries meet: the one that feeds blood to the brain and the one where your brain tissue starts. Once the cold hits those arteries, they dilate and contract rapidly, which causes the receptors in the brain’s outer membrane to feel a burning pain. Here are tips for getting rid of a brain freeze (and other pesky problems).
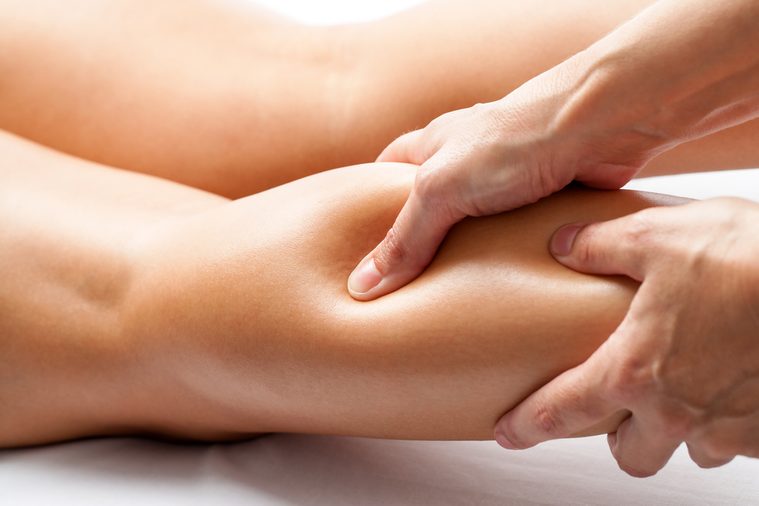

You get a “Charley horse”
A Charley horse is a fancy nickname for a painful muscle cramp, commonly in your calf. Research estimates that one in three people get these brief, uncontrollable muscle spasms in their legs. For non-disease related muscle cramps, the exact reason is still unknown, but some experts think the muscles might be squeezing up because the nerves are firing off in the muscles. One study to support this theory found that the nerves inside the muscles fire off at high rates of up to 150 electrical charges per second, which forces the muscle to squeeze tightly and cramp up.
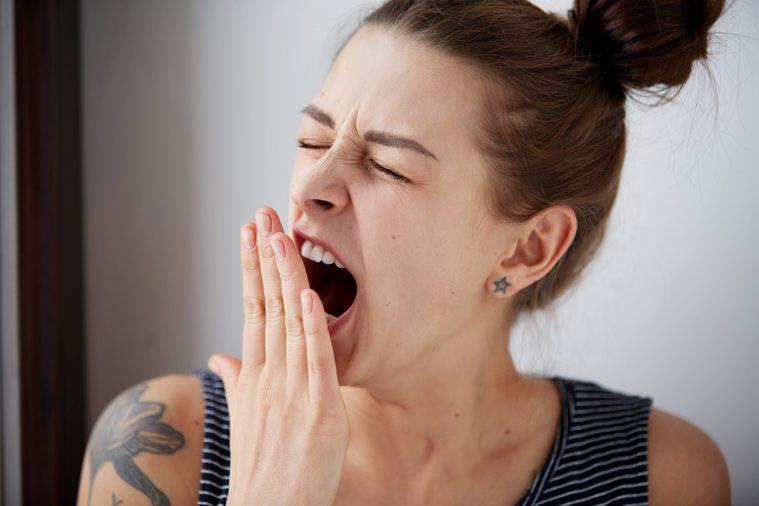

Your eyes tear up when you yawn
A film of lubricating tears coats your eyes, but whenever it builds up the tears can drain into the two tiny openings at the inner corners of your eyes. Yawning can actually block these openings because of the muscular tension that occurs when you close your eyes to yawn. A few tears may stream down your face because of this temporary blockage. Brush up on your science knowledge with these obscure facts about the human body that no one ever told you.
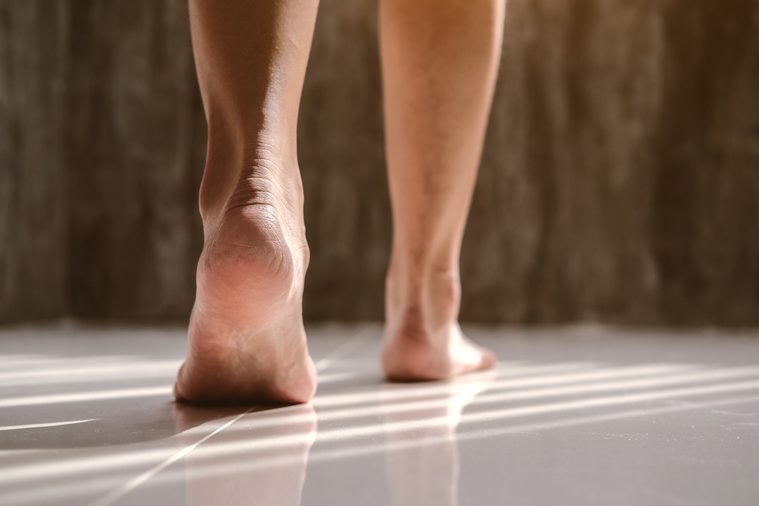

Your foot gets numb after sitting in the same position for a long time
The pins and needles you feel after getting up from sitting in a criss-cross position on the couch for too long are actually caused by a pinching or pressure in the nerves that can hinder blood flow to that limb. And apparently, if you’re thinner you’re more likely to experience that tingling limb feeling because there’s not as much body fat to cushion the blood vessels in your limbs to prevent them from getting compressed when you sit. Learn more about what happens when your foot falls asleep.
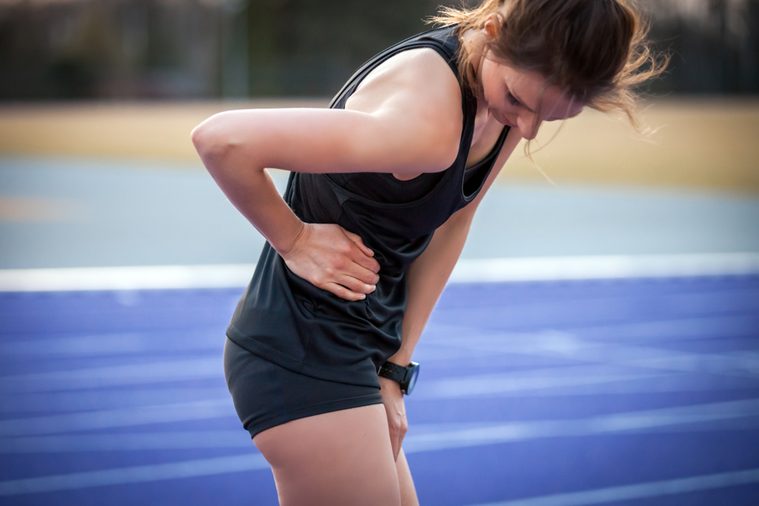

You get a stitch in your side from running
“A side stitch is caused by irritation to the diaphragm, the muscle that separates the lung cavity from the abdominal cavity,” says Dr. Rantala. Starting a new running routine can cause pressure to push up or down on the diaphragm from the abdomen or lungs, respectively. Any kind of pressure to the diaphragm can restrict blood flow and cause it to spasm. Once your body gets used to the exertion, the side stitches should eventually cease unless you eat a fatty meal before a run. A greasy hamburger for a pre-run snack will fill up your stomach and pull down on the diaphragm causing it to spasm. Here are some healthy breathing tips to help you avoid getting stitches in the first place.
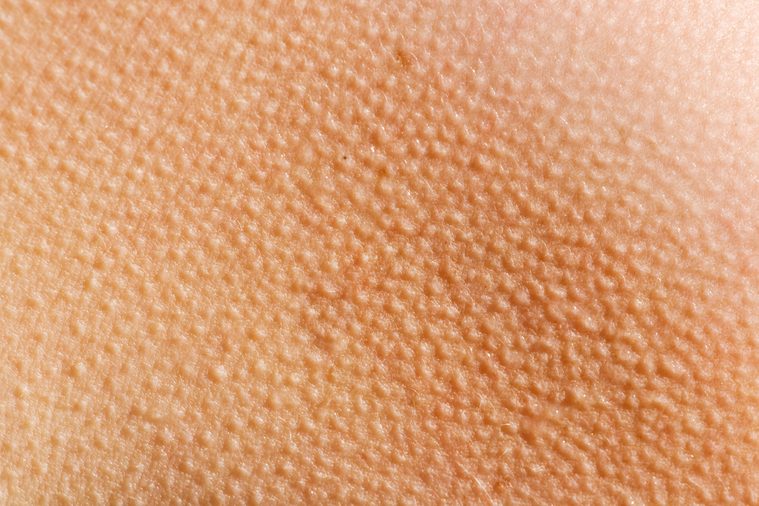

You get goosebumps when you’re scared
Humans inherited goosebumps from our animal ancestors. In terms of survival or longevity, goosebumps are futile. When you’re watching a scary movie or feel chilly, a surge of adrenaline, the stress hormone, is released into your body, which causes the teeny skin muscles at the base of each hair follicle to contract and make our body hair stand up. Even though this mechanism is useless for us, it comes in handy for animals because a raised fur coat helps insulate them from the cold or makes them look bigger to predators in times of distress.
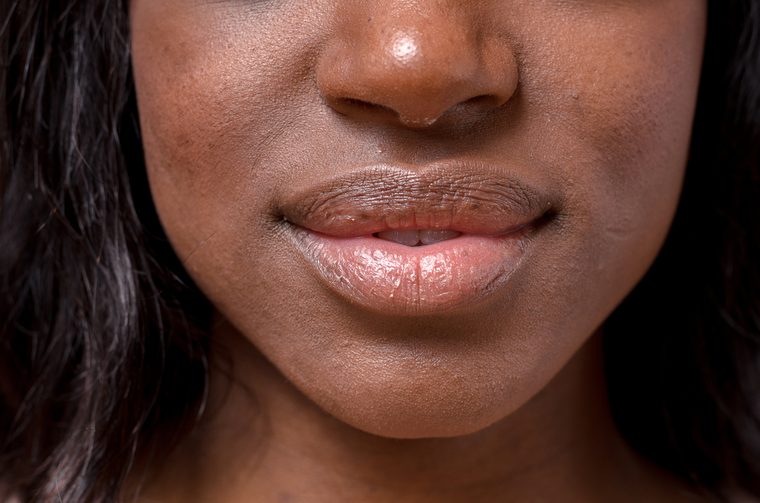

Your lips get chapped in the cold
Your pout is much more susceptible to dry skin because the skin on your lips is thinner than other body parts. And much like the palms of your hands and soles of your feet, your lips don’t have as many oil-producing glands as the rest of your body to keep your lips moist. The moral of the lesson here: keep applying that chapstick! Check out these body parts that are way younger than your actual age.
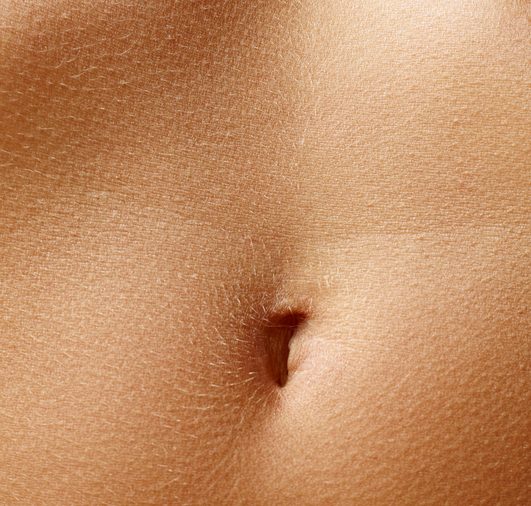
Your stomach growls when you’re hungry
The growling sounds and rumbly tummy feeling associated with hunger pangs are actually just stomach contractions. When the receptors in the stomach walls sense an absence of food, they send out a reflex of electrical waves throughout the stomach and small intestines, which cause the muscular walls of the stomach to squeeze and release.
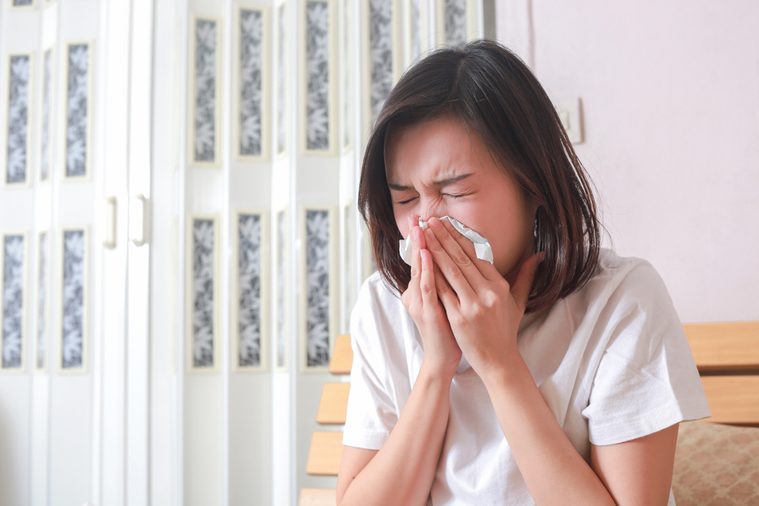

You sneeze when you look up at the sun
Photic sneeze reflex or sun sneeze is the term for this peculiar phenomenon. “The theory is that the optic nerve, which senses a change in light, is very close to the trigeminal nerve, which controls a sneeze,” says Dr. Rantala. You sneeze to expel irritants in the nose. When you step out of a dark room into a bright light your optic nerve starts to constrict your pupils, but this rapid triggering may also give the sensation that there is an irritation in the nose and results in a sneeze. Oddly enough, not everyone has sun sneeze. And it’s not known why some people do and some people don’t. Here are more strange body facts you always wondered about.

You see spots after a camera flashes
The photoreceptors in the back of your eye convert light into electrical impulses that are sent to the brain to produce the images you see every day. “When a camera flash goes off, it’s so bright that it’s overstimulating the photoreceptors,” Elaine Icban, assistant professor of clinical optometry at the New England College of Optometry told Stat News. “It takes awhile for those photoreceptors to get back to normal so the eyes see the afterimage of that flash.”

You get dizzy if you stand up too quickly
You may feel lightheaded sometimes if your body can’t regulate your blood pressure quick enough when you stand up. Blood will briefly pool in your legs after you stand up because of gravity. In an effort to compensate for the low blood flow to your brain, your body will quickly increase your heart rate and constrict your blood vessels to get your blood pressure back to normal again. Your body usually can do this in record time before dizzy symptoms start to develop, but it may sometimes take a moment longer to readjust. Here are some surprising home remedies for dizziness you should keep on hand.
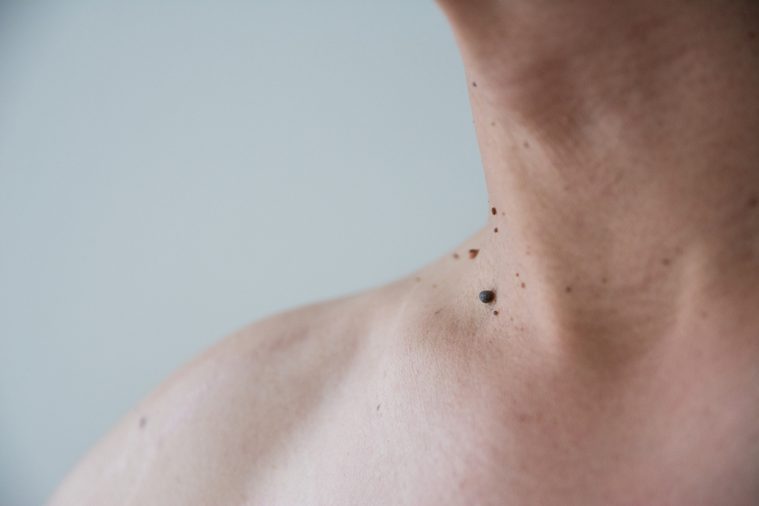
Your moles grow thicker, longer hair than other parts of your body
Moles are nothing more than a cluster of pigment-producing cells in the skin. Sometimes, they lay on top of a hair follicle. Due to this hyperpigmentation, the hair can grow to be coarser and darker.
You grow wisdom teeth
Wisdom teeth are actually a third set of molars. They allowed our forebearers to munch on rough food such as roots, nuts, and meat, especially when other teeth fell out (alas, our ancestors had poor oral hygiene). About 35 percent of people never develop wisdom teeth, partly because of an evolutionary shift that means the human jaw is often too small for them. The rest of us start developing them by age ten, though they don’t fully emerge until young adulthood, which is when we (allegedly) acquire full-grown wisdom. If you have to get yours removed, be sure to have the best foods to eat after wisdom teeth removal on hand.

You get that stomach-in-your-throat feeling on a roller coaster
When a coaster comes over a crest and plummets, the seat belt may keep your rear in place, but some loosely connected internal organs—such as your stomach and intestines—get a little “air time.” Your nerves detect the movement, which registers as the feeling that your stomach has jumped all the way into your throat.
You might smell like a rotten egg after eating meat
Consuming too much meat (particularly red) plus an inability to digest it well can lead to a sulfurous odor caused by the food’s sulfur-containing amino acids. One small study found that women rated men’s body odors as more attractive, more pleasant, and less intense after they had eaten no meat for two weeks compared with when they’d eaten red meat, according to the University of California, Berkeley. Check out these plant-based protein sources that can help you cut back on your meat consumption.

You blink constantly
The average person blinks 15 to 20 times every minute. Each time you blink, your eyelids spread a cocktail of oils and mucous secretions across the surface of your globes to keep them from drying out. Blinking also keeps eyes safe from potentially damaging stimuli, such as bright lights, and foreign bodies, such as dust.

You shiver when it’s cold out
“Our body is always trying to keep our body temperature as close to 98.6 as possible,” says Dr. Rantala. “We shiver when we are cold because this is a way to quiver our muscles in an effort to create heat.” Shivering is a tactic that involves the contraction and expansion of your muscles in quick bursts to regulate your body temperature. Learn about these body parts you didn’t know you had all your life.
