
Nearly one-third of Americans have stopped taking a prescription drug at some time without consulting their doctor, according to the 2017 NPR-Truven Health Analytics Health Poll. The biggest reason given for not even starting a prescription was cost. Reasons given by survey respondents for discontinuing a medication included: side effects (29%), didn’t need (17%), felt better (16%), not working (15%), and cost (10%).
When you abruptly stop taking a prescription medication without telling your doctor it’s called medication non-adherence, and it is estimated to result in increased hospitalizations and premature deaths, alongside a whopping healthcare bill for America that totals anywhere between $100 billion and $289 billion a year, according to an NPR report. It may seem like the medication isn’t working (maybe the dosage needs to be adjusted) or like you’re feeling better or don’t need it (you won’t be feeling better when the meds wear off and symptoms return). Stopping some medications can cause withdrawal symptoms that leave you feeling worse than when you started. It’s important to always talk with your doctor first before you stop taking any of your prescription medicines, especially the following types of meds.

Blood pressure medications
“Blood pressure medications like beta-blockers are used to keep the heart beating nice and slow,” says Barry Grossman, MD, clinical instructor of medicine at New York University. “If you were to stop taking it suddenly the beta-blocker could have a rebound effect like a racing heart.” In fact, a rebound episode could result in ischemia of the heart and a dramatic rise in blood pressure and heart rate. All of which are the building blocks for a heart attack in the future. Learn exactly what to do if you think you’re having a heart attack.
Blood Thinners
Two to three million Americans take blood thinners, medicines that prevent blood clots from forming, according to WebMD. Blood clots found in your arteries, veins, and heart can cause heart attacks, strokes, and blockages. Anticoagulants like Coumadin, a type of blood thinner, should always be taken as directed and never stopped without your doctor’s knowledge. “Every doctor I’ve known who has patients that have run out or decided they didn’t want to take [their anticoagulant] anymore had a stroke because they stopped [taking it],” says Grossman.
Anti-anxiety medications
Benzodiazepines are the most prominently used class of anti-anxiety drugs. Even though the drug is great at providing immediate relief against anxiety symptoms, don’t be fooled into believing that you can stop taking them once your anxiety has ceased. “With long term use and frequent use of these drugs, a physiological dependence can develop,” says David Henderson, MD, professor chair of psychiatry at Boston University School of Medicine. “The abrupt stopping in that class could lead to consequences like withdrawal symptoms similar to alcohol withdrawal and even seizures.” Your risk of seizures is greatest during the first 24 to 72 hours after you stop. In order to prevent these withdrawal symptoms and seizure risk, your doctor will slowly taper your dosage until your body is safely off the drug entirely. Before you head to the pharmacy, make sure you know the most expensive prescription drugs in America.

Antidepressants
Withdrawal symptoms from antidepressants aren’t nearly as dangerous as anti-anxiety meds, but they’re still very uncomfortable. You’re likely to experience headaches, lightheadedness, nausea, and sweating. “The risk of relapse is a great concern,” says Henderson. The general rule of thumb for antidepressants: If a patient’s symptoms improve after taking the medication for six months to a year, then the doctor can consider tapering them off. Tapering is important; the faster you quit antidepressants cold turkey, the more you increase your risk of relapsing back into a depression again. “There’s an incentive to find the right treatment, stay on that treatment, and prevent the illness from coming back,” says Henderson. “But with more relapses, it’s hard to get the quick response and more difficult to get them well.” This is what to do when you feel your antidepressants aren’t working.
Steroids
Your body’s adrenal glands make a natural steroid hormone called cortisol, a powerful anti-inflammatory. But sometimes we need an extra punch of steroids in our bodies to fight off an acute illness or inflammation. This is when prescription steroids, like the commonly used prednisone, are valuable. Grossman describes prednisone as a “double-edged sword” because when you start taking the medication “your adrenal glands will say, ‘Hey, we’re getting the steroid from a pill. Let’s go on vacation.’” If you stop taking the steroid suddenly, your body’s adrenal glands will need about a week or two to wake up and start making cortisol again. Weakness, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain may ensue, due to the low levels of cortisol in your system. A doctor can slowly wean you off of the steroids and ease your body back into making cortisol on its own again without the horrible withdrawal effects. Prednisone is a medication where the dose has to be right or it could make you sick.

Opioid pain medications
Codeine, morphine, and hydrocodone are opioids that doctors prescribe to treat pain. “If someone has taken it for months at a substantial dose, when they stop it, they’re going to go in withdrawal which is the same as seeing someone who is using heroine on the street,” says Grossman. Restlessness, anxiety, diarrhea, and generalized pain are just a few of the withdrawal symptoms someone may experience if they stop taking opioids cold turkey. Once again, your doctor can taper the dosage until you’re off the medication completely and help you avoid unpleasant withdrawal symptoms. If you are being prescribed opioids for the first time, ask about alternatives. Opioids are just one of the 14 pain medications doctors always try to avoid taking themselves.
Eye drops for glaucoma
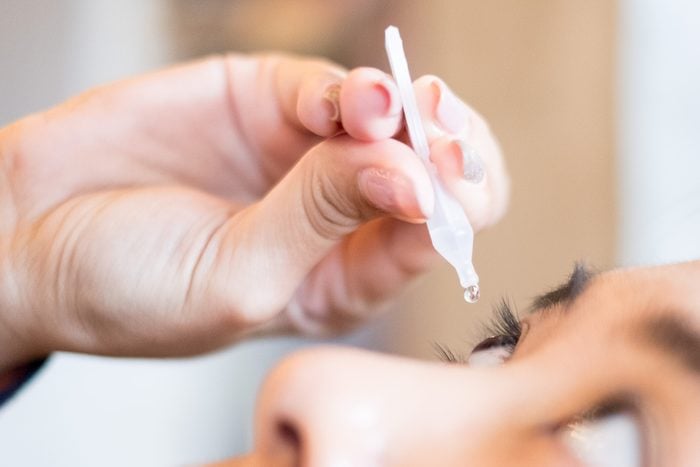
Glaucoma is an eye disease that is caused by fluid buildup in the front portion of your eye, which can damage the eye’s optic nerve needed for sight. According to the National Eye Institute, the number of people in the U.S. with glaucoma will more than double by 2050 to 6.3 million people. “Eye drops help decrease the pressure in the eyes,” says Grossman. “But some people get tired of putting drops in their eyes and the eye pressure will go back to the way it was.” If the pressure from the fluid buildup continues, it can further damage the eye’s optic nerve and potentially lead to blindness in the future.
Anticonvulsants
People who take anti-seizure medications should never discontinue them abruptly as it can also create a rebound effect and greatly increase your seizure frequency. For some other anti-seizure medications, you may experience withdrawal symptoms within the next 24 to 48 hours. Agitation, confusion, and disorientation are some of the most commonly reported withdrawal symptoms.

Thyroid medication
People with hyperthyroid (overactive thyroid) and hypothyroid (underactive thyroid) need medication to regulate their thyroid’s hormone production, which helps control metabolism. People with hyperthyroid who stop taking their medications may trigger a “thyroid storm.” A life-threatening condition accompanied by a rapid heartbeat, fever, fainting, and if left untreated, coma. Now that you know the side effects from stopping certain medications cold turkey, check out the truly bizarre side effects caused by 10 common medications, including thyroid meds.